Discover how Tenmat’s FF107 advanced intumescent material is used in ember-resistant vents, fire collars, pipe and duct fire wraps to bring the presence of passive fire protection into a wide range of industries.
In today’s world of construction, intumescents are no longer unfamiliar material in the practice of passive fire protection. Known for their versatility and adaptability, intumescent materials have become one of the key components in the development of advanced passive fire protection solutions.
Developed to meet various expansion ratios + char output, Tenmat’s Advanced Intumescent Materials and Solutions are built to handle diverse and complex applications with ease. From mass timber construction to ember-resistant vents, our advanced intumescent materials have been utilized in passive fire protection solutions to meet the rigorous demands of a broad range of applications.
Among our portfolio, Tenmat’s FF107 material is considered one of the most versatile intumescent materials we offer. Let’s take a closer look at how Tenmat’s FF107 is redefining the standards of fire protection, from its ability to protect a building from both external and internal fire outbreaks.
Why Should You Develop with the FF107 Material?
TENMAT FIREFLY 107 is a high-performance intumescent material engineered for rapid activation and powerful expansion under heat exposure. Its unique formulation delivers a fast reaction time, generating a high level of pressure and volume to form a strong barrier against heat and flame spread.

What sets FF107 apart from other traditional firestopping methods is its ability to produce a dense, solid char with excellent structural integrity – ensuring consistent protection and durability in demanding life safety conditions.
In addition to its high expansion and pressure generation characteristics, the FF107 has been tested according to ASTM E84 (UL 723) to measure its surface burning characteristics and achieved a Flame Spread Index of 0 and Smoke Developed Value of 0.
Tenmat FF107 is tested according to the current UL requirements and is a Recognized Component under UL Category OEXX2 for Intumescent Materials – Component. This combination of fast response, high expansion, and reliable char formation makes FireFly FF107 a trusted fire-rated material to use in the creation of fire-resistance rated applications.
How does Tenmat apply its FF107 material in mass timber construction?

As the International Building Council (IBC) adopts more sustainable construction practices, architects and engineers have been challenged to integrate these standards into their designs. In response to this shift, innovative building methods have gained traction – one of the most prominent being mass timber construction.
Mass timber construction is built using a category of engineered wood products typically made of large, solid wood panels, columns or beams often manufactured off-site for load-bearing wall, floor, and roof construction.
It offers sustainability, design flexibility, efficiency, structural performance, and a myriad of other advantages, which position it as a prime candidate for sustainable building practices.
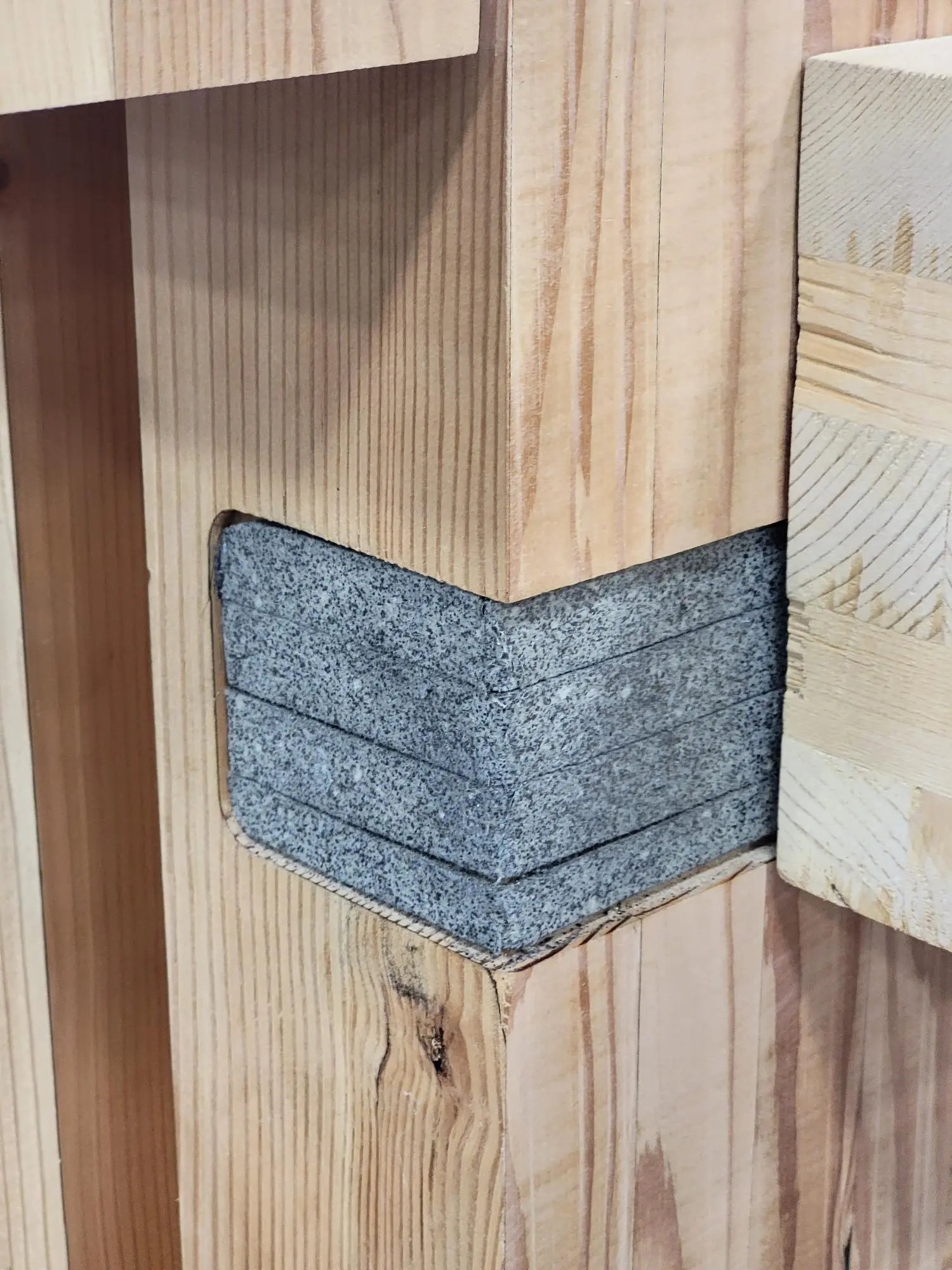
For joint and gap sealing applications in cross-laminated timber (CLT), and glulam, Tenmat has developed a state-of-the-art intumescent material, the FF107.
Tenmat’s FIREFLY 107 is an exceptionally powerful intumescent which combines fast reaction with high expansion and pressure generation – producing a solid char of good integrity. With its composition, the FF107 is applicable in construction joints and gaps.
When specified into construction joints and gaps, the FF107 slows the acceleration of flame and heat spread during an outbreak – ensuring these gaps do not compromise the structure’s integrity.
Learn More about Tenmat’s FF107 in Mass Timber Construction Here.
How does FF107 play a role in Ember-Resistant Vents?

In high-risk wildfire zones (WUI zones), California building code officials now require new construction buildings to incorporate ember-resistant vents into their residential designs. Why? To protect residential homes from self-igniting during a wildfire outbreak.
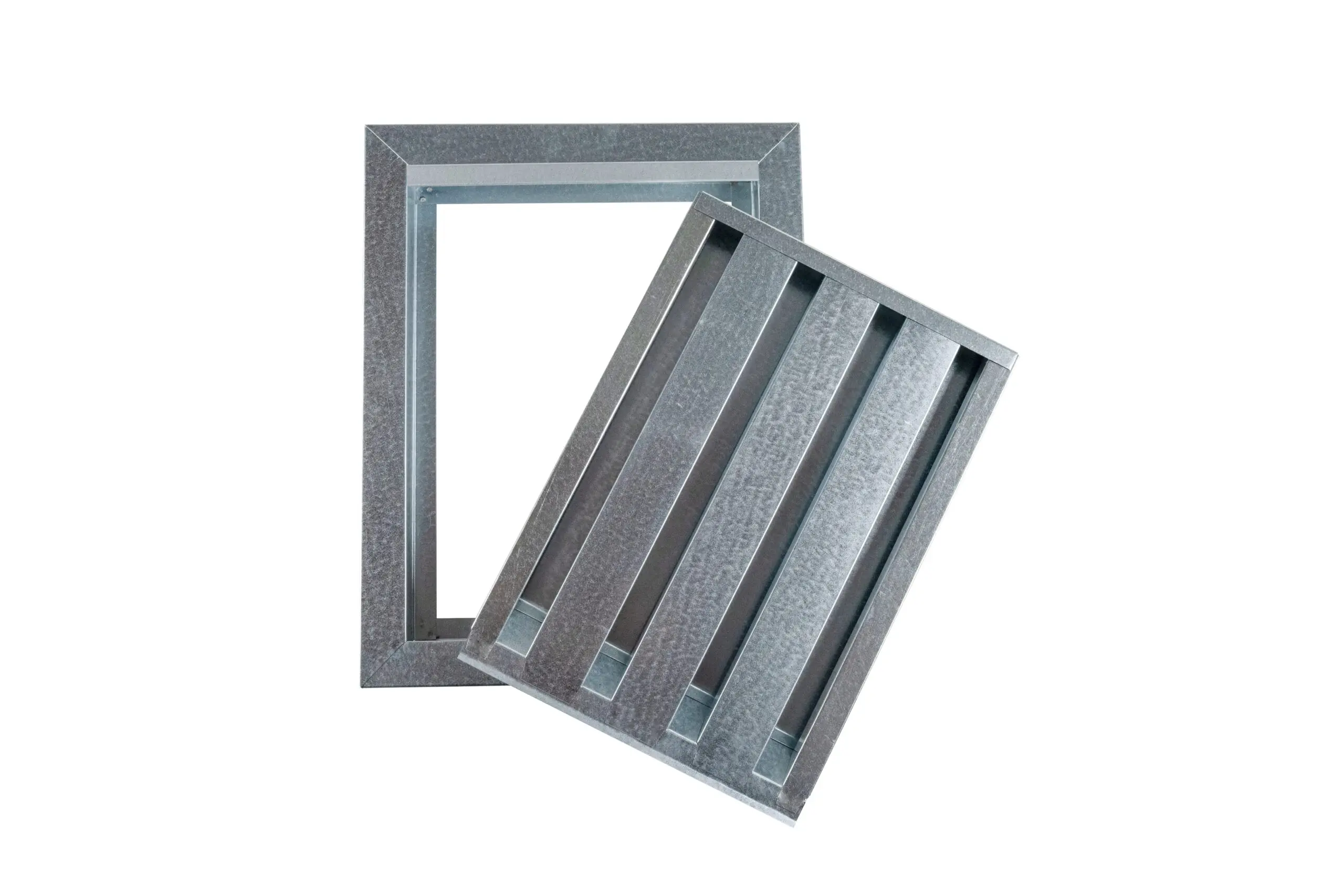
When homeowners integrate an air ventilation system into their homes, each one of the vents act as prime entry point for hot embers and flames. To protect these entry points without compromising the air flow, homeowners install ember-resistant vents, such as BrandGuard Vents, into their residences to keep out these unwanted guests.
Now, here is where Tenmat FF107 plays a major role. Unlike other ember-resistant vent technology, BrandGuard incorporates Tenmat’s FF107 strips into its vent’s technology. When temperatures rise to dangerous levels in a wildfire, these strips expand rapidly to seal vent openings. This reaction effectively blocks embers and prevents flames from entering one’s household.
With the FF107’s fast reaction and highly expansive properties, BrandGuard’s Ember-Resistant Vents can react when it matters most.
Explore BrandGuard Vents Ember- and Flame-Resistant Vents.
Learn more about California’s Chapter 7A.
Final Notes
With its rapid expansion, high-pressure generation, and solid char formation, Tenmat’s FF107 material delivers reliable performance across a wide range of applications – from sealing off gaps in mass timber construction to safeguarding homes in WUI zones through ember-resistant technology.
As building codes and fire safety regulations evolve, the demand for advanced fire-resistant materials continues to grow. Tenmat leads the way with innovative products like FF107, helping builders, architects, and homeowners enhance fire resilience and meet modern safety standards.