Discover how to identify the “when and where” of specifying fireblocking within your modern ventilated rainscreen application.
In our previous blog, When is fireblocking required in ventilated rainscreen systems?, we took a deep dive into understanding the various building code regulations that would cause a trigger for the requirement of fireblocking. If you missed this piece, we highly suggest reviewing before moving forward in this series.
Read the first article in the Intumescent Fireblocking Educational Series, “When is fireblocking required in ventilated rainscreen systems?”.
With your ability to identify on when fireblocking is required in your ventilated rainscreen system, now we are going to challenge you to learn the next step – the placement of fireblocking in your façade application.
What are the IBC requirements for fireblocking placement?
In the International Building Code or IBC, the language can be rather broad in certain areas. But one thing for certain is the IBC code language is very clear when it comes to the placement of fireblocking in the cavity.
In Section 718.2.6 of the International Building Code, it states that:
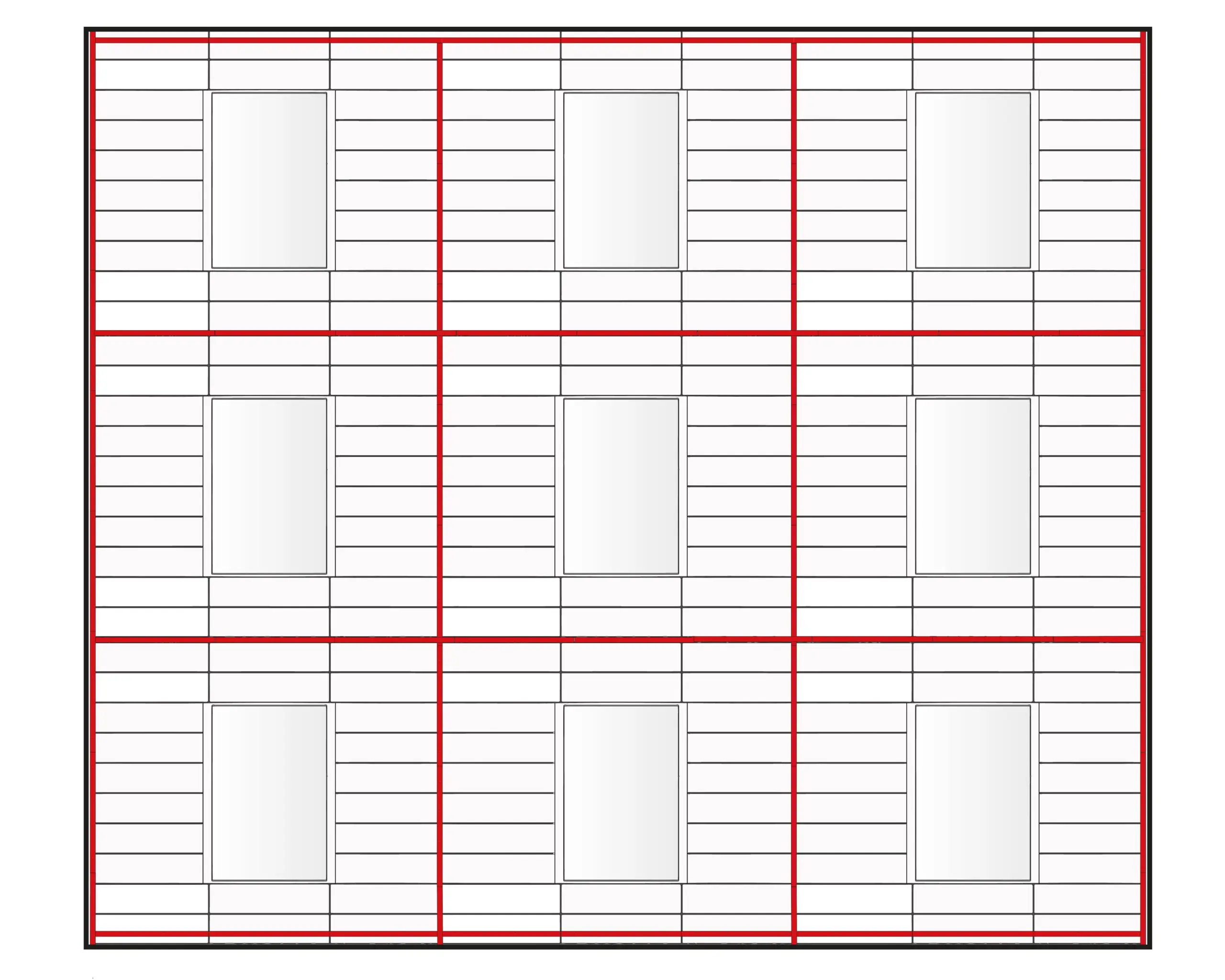
“Fireblocking shall be installed at maximum intervals of 20 feet (6096 mm) in either dimension so that there will be no concealed space exceeding 100 square feet (9.3 m2) between fireblocking”
This language indicates that fireblocking must be installed in both vertical and horizontal orientations to create compartments that don’t exceed 100 square feet – but don’t excess 20 LF in either direction (refer to Figure 1).
Is the placement of fire blocking the same in every state in the United States?
While the International Building Code clearly outlines the requirements for fireblocking placement, this does not mean individual jurisdictions cannot not or will not make modifications for in the adoption of building codes.
In year of 2022, New York City made numerous modifications to Section 718.2.6 regarding the placement and building materials used in modern ventilated rainscreen assemblies. To give a bit of context on just how many details NYC modified, we took a snapshot of the modifications in Figure 2. The adoptions and modifications of the NYC building code will be reviewed further in depth later in the series.

Figure 2: The 2022 NYC Building Code Section 718.2.6 is being showcased. The highlighted pink text is all the modifications NYC Building Department applied to Section 718.2.6.
How do you know if your local jurisdiction has modified the placement of fireblocking?
Just like with any other specification questions, consult with your local building code department. They will guide you in the right direction regarding the requirements AND the placement of fire blocking in your application.
However, if you want a quick and effortless answer, check out the platform UpCodes. This platform provides easy access to 8,000+ building codes and standards for architects, engineers, and contractors.
What’s Next?
With a better understanding of the placement requirements and where fire-blocking is incorporated into the design, installation questions come to light. With many of the components engineered and installed based on the needs of the assembly, exterior wall covering assemblies are rarely evenly spaced – like a stud wall configuration.
Installing traditional fireblocking materials around all these components, in addition to achieving the tight fit, turns into its own individual challenge – and we haven’t even touched on the performance issues. Resolve this conflict in our next blog in the Intumescent Fireblocking Educational Series.





